A function is similar to a normal procedure but the main purpose of the function is to accept a certain input from the user and return a value which is passed on to the main program to finish the execution. There are two types of functions, the built-in functions (or internal functions) and the functions created by the programmers.
The general format of a function is
FunctionName (arguments)
FunctionName (arguments)
The arguments are values that are passed on to the function.
In this lesson, you will learn two very basic but useful internal functions of Visual basic , i.e. the MsgBox( ) and InputBox ( ) functions.
The objective of MsgBox is to produce a pop-up message box that prompt the user to click on a command button before he /she can continues. This format is as follows:
yourMsg=MsgBox(Prompt, Style Value, Title)
The first argument, Prompt, will display the message in the message box. The Style Value will determine what type of command buttons appear on the message box, please refer Table 10.1 for types of command button displayed. The Title argument will display the title of the message board.
Style Value | Named Constant | Buttons Displayed |
| vbOkOnly | Ok button | |
| vbOkCancel | Ok and Cancel buttons | |
| vbAbortRetryIgnore | Abort, Retry and Ignore buttons. | |
| vbYesNoCancel | Yes, No and Cancel buttons | |
| vbYesNo | Yes and No buttons | |
| vbRetryCancel | Retry and Cancel buttons |
We can use named constant in place of integers for the second argument to make the programs more readable. In fact, VB6 will automatically shows up a list of names constant where you can select one of them.
Example: yourMsg=MsgBox( "Click OK to Proceed", 1, "Startup Menu")
and yourMsg=Msg("Click OK to Proceed". vbOkCancel,"Startup Menu")
are the same.
yourMsg is a variable that holds values that are returned by the MsgBox ( ) function. The values are determined by the type of buttons being clicked by the users. It has to be declared as Integer data type in the procedure or in the general declaration section. Table 10.2 shows the values, the corresponding named constant and buttons.
Table 10.2 : Return Values and Command Buttons
| Named Constant | Button Clicked | |
| vbOk | Ok button | |
| vbCancel | Cancel button | |
| vbAbort | Abort button | |
| vbRetry | Retry button | |
| vbIgnore | Ignore button | |
| vbYes | Yes button | |
| vbNo | No button |
Example 10.1
i. The Interface:
You draw three command buttons and a label as shown in Figure 10.1
Figure 10.1
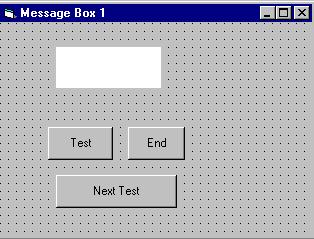
ii. The procedure for the test button:
Private Sub Test_Click()
Dim testmsg As Integer
testmsg = MsgBox("Click to test", 1, "Test message")
If testmsg = 1 Then
Display.Caption = "Testing Successful"
Else
Display.Caption = "Testing fail"
End If
End Sub
When a user click on the test button, the image like the one shown in Figure 10.2 will appear. As the user click on the OK button, the message "Testing successful" will be displayed and when he/she clicks on the Cancel button, the message "Testing fail" will be displayed.

To make the message box looks more sophisticated, you can add an icon besides the message. There are four types of icons available in VB as shown in Table 10.3
| Named Constant | Icon | |
| vbCritical | ||
| vbQuestion | ||
| vbExclamation | ||
| vbInformation |
Example 10.2
You draw the same Interface as in example 10.1 but modify the codes as follows:
Private Sub test2_Click()Dim testMsg2 As Integer
testMsg2 = MsgBox("Click to Test", vbYesNoCancel + vbExclamation, "Test Message")
If testMsg2 = 6 Then
display2.Caption = "Testing successful"
ElseIf testMsg2 = 7 Then
display2.Caption = "Are you sure?"
Else
display2.Caption = "Testing fail"
End IfEnd SubIn this example, the following message box will be displayed:
Figure 10.3
10.2 The InputBox( ) Function
An InputBox( ) function will display a message box where the user can enter a value or a message in the form of text. The format is
myMessage=InputBox(Prompt, Title, default_text, x-position, y-position)
myMessage is a variant data type but typically it is declared as string, which accept the message input by the users. The arguments are explained as follows:
- Prompt - The message displayed normally as a question asked.
- Title - The title of the Input Box.
- default-text - The default text that appears in the input field where users can use it as his intended input or he may change to the message he wish to key in.
- x-position and y-position - the position or the coordinate of the input box.
i. The Interface
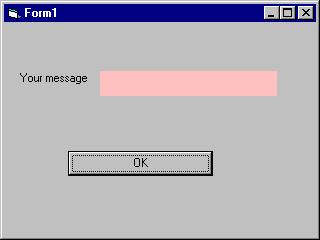
ii. The procedure for the OK button
Private Sub OK_Click()When a user click the OK button, the input box as shown in Figure 10.5 will appear. After user entering the message and click OK, the message will be displayed on the caption, if he click Cancel, "No message" will be displayed.
Dim userMsg As StringEnd Sub
userMsg = InputBox("What is your message?", "Message Entry Form", "Enter your messge here", 500, 700)
If userMsg <> "" Then
message.Caption = userMsg
Else
message.Caption = "No Message"
End If
http://www.vbtutor.net/vb6/vbtutor.html


No comments:
Post a Comment