n Lesson 22 and Lesson 23, we have learned how to build VB database applications using data control. However, data control is not a very flexible tool as it could only work with limited kinds of data and must work strictly in the Visual Basic environment.
To overcome these limitations, we can use a much more powerful data control in Visual Basic, known as ADO control. ADO stands for ActiveX data objects. As ADO is ActiveX-based, it can work in different platforms (different computer systems) and different programming languages. Besides, it can access many different kinds of data such as data displayed in the Internet browsers, email text and even graphics other than the usual relational and non relational database information.
To be able to use ADO data control, you need to insert it into the toolbox. To do this, simply press Ctrl+T to open the components dialog box and select Microsoft ActiveX Data Control 6. After this, you can proceed to build your ADO-based VB database applications.
The following example will illustrate how to build a relatively powerful database application using ADO data control. First of all, name the new form as frmBookTitle and change its caption to Book Titles- ADO Application. Secondly, insert the ADO data control and name it as adoBooks and change its caption to book. Next, insert the necessary labels, text boxes and command buttons. The runtime interface of this program is shown in the diagram below, it allows adding and deletion as well as updating and browsing of data
To be able to access and manage a database, you need to connect the ADO data control to a database file. We are going to use BIBLIO.MDB that comes with VB6. To connect ADO to this database file , follow the steps below:
a) Click on the ADO control on the form and open up the properties window.
b) Click on the ConnectionString property, the following dialog box will appear.
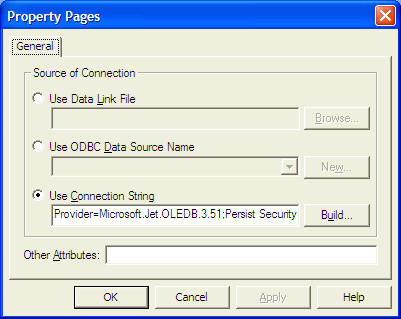
when the dialog box appear, select the Use Connection String's Option. Next, click build and at the Data Link dialog box, double-Click the option labeled Microsoft Jet 3.51 OLE DB provider
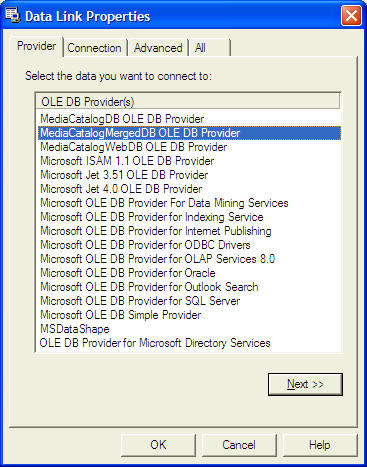
After that, click the Next button to select the file BIBLO.MDB. You can click on Text Connection to ensure proper connection of the database file. Click OK to finish the connection.
Finally, click on the RecordSource property and set the command type to adCmd Table and Table name to Titles. Now you are ready to use the database file.
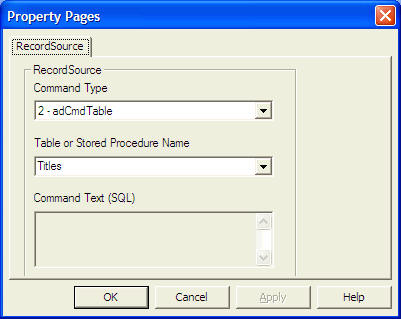
Now, you need to write code for all the command buttons. After which, you can make the ADO control invisible.
Private Sub cmdSave_Click()For the Add button, the program codes are as follow:
adoBooks.Recordset.Fields("Title") = txtTitle.TextEnd Sub
adoBooks.Recordset.Fields("Year Published") = txtPub.Text
adoBooks.Recordset.Fields("ISBN") = txtISBN.Text
adoBooks.Recordset.Fields("PubID") = txtPubID.Text
adoBooks.Recordset.Fields("Subject") = txtSubject.Text
adoBooks.Recordset.Update
For the Delete button, the program codes are as follow:Private Sub cmdAdd_Click()
adoBooks.Recordset.AddNewEnd Sub
For the Cancel button, the program codes are as follow:Private Sub cmdDelete_Click()
Confirm = MsgBox("Are you sure you want to delete this record?", vbYesNo, "Deletion Confirmation")End Sub
If Confirm = vbYes Then
adoBooks.Recordset.Delete
MsgBox "Record Deleted!", , "Message"
Else
MsgBox "Record Not Deleted!", , "Message"
End If
For the Previous (<) button, the program codes arePrivate Sub cmdCancel_Click()
txtTitle.Text = ""End Sub
txtPub.Text = ""
txtPubID.Text = ""
txtISBN.Text = ""
txtSubject.Text = ""
Private Sub cmdPrev_Click()
If Not adoBooks.Recordset.BOF Then
adoBooks.Recordset.MovePrevious
If adoBooks.Recordset.BOF Then
adoBooks.Recordset.MoveNext
End If
End If
End Sub
For the Next(>) button, the program codes are
Private Sub cmdNext_Click()
End Sub
If Not adoBooks.Recordset.EOF Then
adoBooks.Recordset.MoveNext
If adoBooks.Recordset.EOF Then
adoBooks.Recordset.MovePrevious
End If
End If
http://www.vbtutor.net/vb6/vbtutor.html

No comments:
Post a Comment